View Price Ceiling Graph Example
Background. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. A price ceiling example—rent control. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example.
Econport Price Floors And Ceilings
Price Controls Price Floors And Ceilings Illustrated. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below A price ceiling example—rent control. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0.
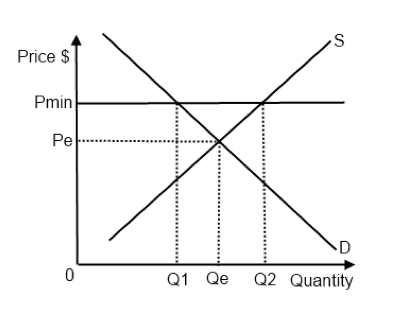
It represents an upper limit on the price of something. An example is a price ceiling on apartment rents, which some cities impose on landlords. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. Another example is the price ceiling on rent specially after second world war when soldiers were free and a price ceiling prevents a price from rising above the ceiling. Let's say i am willing to work at mcdonald's for $5 an hour. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation.
An example of a price floor is minimum wage.
A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. A good example is rent control in new york city (rent control is a price ceiling on rent). Let's say i am willing to work at mcdonald's for $5 an hour. A price ceiling creates deadweight lossdeadweight lossdeadweight loss refers to the loss of economic efficiency when the equilibrium outcome is not achievable or not achieved. Price floors and price ceilings are price controls, examples of government intervention in the free market which changes the market equilibrium. Price controls can be price ceilings or price floors. These laws prohibit charging excessive interest on loans. 14.09.2020 · however, prolonged application of a price ceiling can lead to black marketing and unrest in the supply side. If the equilibrium price is $2 this will lower the price ceiling line on the graph to somewhere below the equilibrium price level. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. ~ goes above equilibrium to ensure fairness to the market ~ *if* it goes below the equilibrium, it results in a shortage (more demand at a lower price). An example of a price ceiling in the united states is rent control. The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. In the graph at right, the supply and demand curves intersect to determine the. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. This law introduced a ceiling wage of £3 in 1925, but it was later abolished in 1968. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. Price ceiling is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market for example: Let's say gotham city sets a price ceiling of $1,000 for a one bedroom apartment, where landlords cannot legally charge higher than that rate. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Here in the given graph, a price of rs. Suppose both supply and demand are linear, with the quantity supplied equal to the price and the quantity demanded equal to one minus the. A price ceiling is a form of price control. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. Another example of price ceilings is that of usury laws. Another example of a price ceiling involved the coulter law regarding the vfl in australia. An example of a price floor is minimum wage. A price ceiling means that the price of a good or service cannot go higher than the regulated consider the example of a price ceiling for apartments in new york.
Price Floor Wikipedia
Price Ceilings Economics. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. A price ceiling example—rent control. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling. The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily.
Binding Price Ceiling
Quantity Supplied Definition. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. A price ceiling example—rent control. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service.
What Price Ceiling Maximizes Consumer Surplus Given That Qd 100 P And Qs P Study Com
Does Non Binding Price Ceiling Effect The Market Economics Stack Exchange. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. A price ceiling example—rent control. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling. For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies.
Price Ceiling Definition Effects Graph And Examples Boycewire
Solved A What Is The Equilibrium Price And Quantity P Chegg Com. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. A price ceiling example—rent control.
4 5 Price Controls Principles Of Microeconomics
What Is A Price Ceiling. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. A price ceiling example—rent control. For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service.
Solved This Is An Example Of A Click To Select Binding Chegg Com
What Is A Price Ceiling. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example. The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. A price ceiling example—rent control. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below However, the rent must remain below equilibrium. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling.
Price Ceilings Deadweight Loss Youtube
Market Equilibrium. For example, price ceiling occurs in rent controls in many cities, where the rent is decided by the governmental agencies. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless a price ceiling prevents the the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. Consider a hypothetical market the supply and demand schedules of which are given below The following table shows the changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded at each price for the in the graphs above, we saw what happens when a rent control law is passed to keep the price at the original equilibrium of $500 for a typical apartment. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. Usually set by law, price ceilings are typically applied a price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. A price ceiling example—rent control. The graph shows a shift in demand with a price ceiling. Rent control is a prominent price ceiling example. Examples of price ceiling include price limits on gasoline, rents, insurance premium etc. A price ceiling is the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service. The rent is allowed to rise at a specific rate each year to keep up with inflation. The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. The local government can limit how much a landlord can charge a tenant or by how much the landlord can increase prices annually. However, the rent must remain below equilibrium.