23+ Price Ceiling And Price Floor Real Life Examples
Gif. The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. Price ceiling and price floor example. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. In professional sports, a salary cap (or wage cap) is an agreement or rule that places a limit on the amount of money that a team can. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. In certain markets, demand outstrips supply. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing the opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor, which sets a minimum price at which a product or oil companies would have bumped up production, due to the higher prices, and consumers, who now. A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level.
Price Ceiling And Price Floor Examples Pregnancy Test Kit
Solutions To Price Ceiling And Price Floor In Malaysia Buffer Stock Scheme Black Market Economies. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing the opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor, which sets a minimum price at which a product or oil companies would have bumped up production, due to the higher prices, and consumers, who now. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. Price ceiling and price floor example. A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. In professional sports, a salary cap (or wage cap) is an agreement or rule that places a limit on the amount of money that a team can. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0. The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. In certain markets, demand outstrips supply. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government.
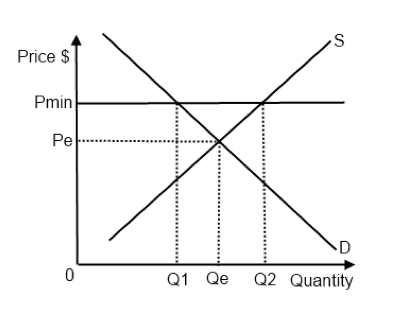
A price floor is said to exist when the price is set above the equilibrium price and is not allowed to fall. Like price ceiling, price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government. But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity. Mathematically, the price ceiling creates a range over which marginal revenue is equal to price (since over this range the monopolist doesn't have to lower price in order to sell more). Price ceilings set the maximum price that can be charged on a product or service. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. The market for butter in europe, in which european governments enforce a price floor.
This work has been submitted by a student.
They are afraid of those farmers start grow others good instead. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. Price floors cause a deadweight welfare loss.a deadweight welfare loss occurs whenever there is a difference between the price the marginal. Secondhand clothing are taxicab rides in new york city expensive or inexpensive in relative terms? Like price ceiling, price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government. It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very. In addition to price controls, governments can also set price floors, as well. Another example of price ceilings is rent control. Price floors and price ceilings are price controls, examples of government intervention in the free market which changes the market equilibrium. Price ceilings are usually government policies and limits that intend to save consumers from being charged too high a price. A price ceiling example—rent control. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. It is used by the government to prevent the prices from. Because nothing in life is free, the cost of a price ceiling program is chronic excess supply. Examples of price ceiling include price. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0. A minimum wage law is another example of a price floor. But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity. Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low. Small farmers are very sensitive to changes in the. Chinese government set a price floor on rice. The governments impose price floors in agriculture in order to convince farmers to keep farming rice. However, price ceilings and price floors do promote equity in the market. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. Price ceilings and price controls consist of maximum or minimum prices imposed by government, intended to help either the consumers or the in this lesson we will look at two real world examples of price controls: Price ceilings set the maximum price that can be charged on a product or service. Price ceilings and price floors let's review! Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. Price floorsa price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at.
Price Floor Wikipedia
Price Floors And Ceilings. A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing the opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor, which sets a minimum price at which a product or oil companies would have bumped up production, due to the higher prices, and consumers, who now. The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. Price ceiling and price floor example. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. In certain markets, demand outstrips supply. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government. In professional sports, a salary cap (or wage cap) is an agreement or rule that places a limit on the amount of money that a team can. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control.
What Is Price Floor Definition Of Price Floor Price Floor Meaning The Economic Times
Chapter 8 Price Ceilings And Floors 1 Price Ceilings. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing the opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor, which sets a minimum price at which a product or oil companies would have bumped up production, due to the higher prices, and consumers, who now. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. In professional sports, a salary cap (or wage cap) is an agreement or rule that places a limit on the amount of money that a team can. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. Price ceiling and price floor example. In certain markets, demand outstrips supply.
Price Controls Price Floors And Ceilings Illustrated
Real Life Example Of A Price Ceiling. Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing the opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor, which sets a minimum price at which a product or oil companies would have bumped up production, due to the higher prices, and consumers, who now. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. Price ceiling and price floor example. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. In professional sports, a salary cap (or wage cap) is an agreement or rule that places a limit on the amount of money that a team can. The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. In certain markets, demand outstrips supply. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0.
Microeconomics 02 Price Control
4 2 Government Intervention In Market Prices Price Floors And Price Ceilings Principles Of Economics. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government. The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing the opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor, which sets a minimum price at which a product or oil companies would have bumped up production, due to the higher prices, and consumers, who now. In certain markets, demand outstrips supply. Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. Price ceiling and price floor example. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. In professional sports, a salary cap (or wage cap) is an agreement or rule that places a limit on the amount of money that a team can. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price.
Price Floor Intelligent Economist
Reading Inefficiency Of Price Floors And Price Ceilings Microeconomics. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0. A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing the opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor, which sets a minimum price at which a product or oil companies would have bumped up production, due to the higher prices, and consumers, who now. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. In professional sports, a salary cap (or wage cap) is an agreement or rule that places a limit on the amount of money that a team can. Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. In certain markets, demand outstrips supply. Price ceiling and price floor example. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price.
Econ 150 Microeconomics
Price Floors And Ceilings. In certain markets, demand outstrips supply. The theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Many agricultural goods have price floors imposed by the government. Price ceiling and price floor example. In professional sports, a salary cap (or wage cap) is an agreement or rule that places a limit on the amount of money that a team can. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing the opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor, which sets a minimum price at which a product or oil companies would have bumped up production, due to the higher prices, and consumers, who now. A price floor is a minimum price at which a product or service is permitted to sell. Although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will the graph shows an example of a price floor which results in a surplus. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. Price floor is the minimum price of a producer is allowed to charge for a product or service.usually the price ceiling is under the equilibrium point. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. The intersection of demand, d, and supply, s, would be at the equilibrium point e0.






