18+ Price Ceiling And Price Floor Pdf
Images. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism.
Price Controls In A Competitive Industry And Monopoly Markets
Prinecomi Lectureppt Ch05. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity.
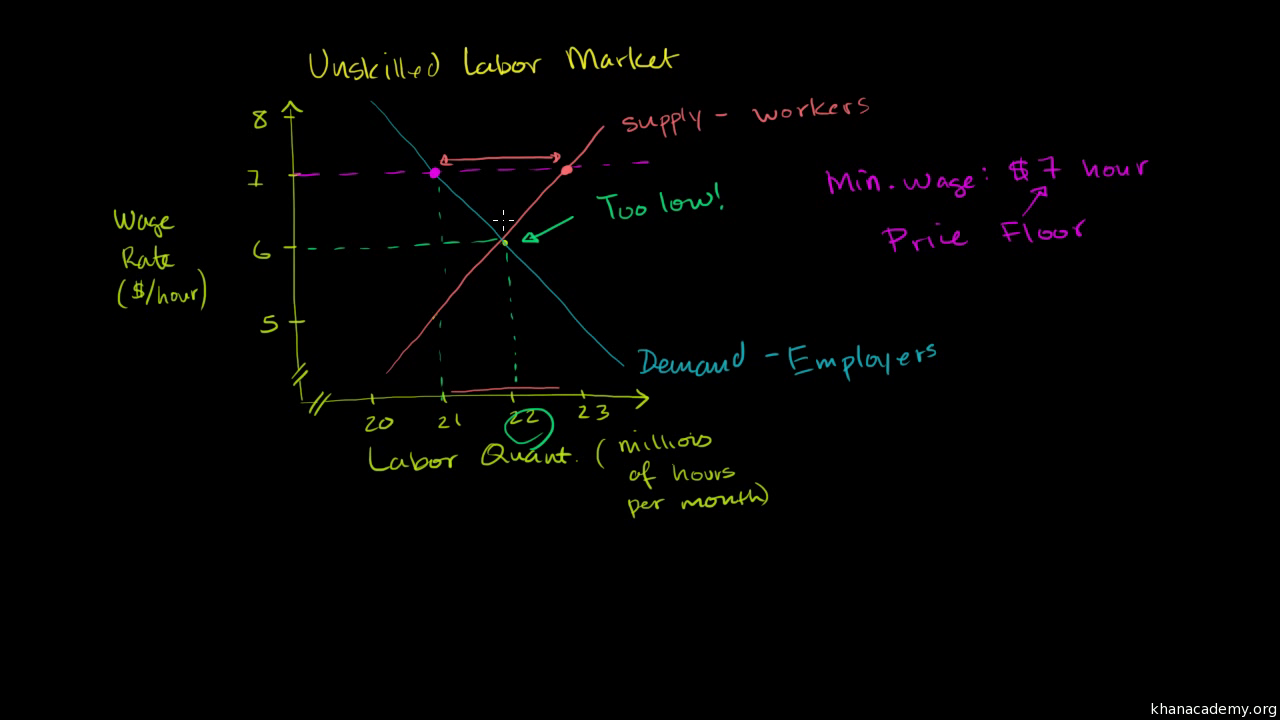
A price ceiling is a: The floor falls under the equilibrium and the ceiling. These products are not just durable but also. A price ceiling can be defined as the price that has been set by the government below the equilibrium price and cannot be soared up above that. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. Price floors are only an issue when they are set above the equilibrium price, since they have no effect if they are set below market clearing price. Floor to ceiling windows are very important parts of any property and hence, need to be strong and durable enough.
Hopefully that answers your questions, about when a price floor & price ceiling will be effective.
Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. A price ceiling is the legal maximum price for a good or service, while a price ceiling below the market price creates a shortage causing consumers to compete vigorously for the limited supply, limited because the quantity supplied declines with price. (note that the price ceiling is represented by the horizontal line labeled pc.) Floor to ceiling windows are very important parts of any property and hence, need to be strong and durable enough. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. Published with reusable license by. A price ceiling creates when it is set the equilibrium price. Legally established minimum price that can be charged for a good. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. All formats available for pc, mac, ebook readers and other mobile devices. A price floor protects producers by keeping prices higher than the market wants. The government then imposes a price floor of $4 on the market. Price floors and ceilings are results of government intervention that causes either a maximum market price (ceiling), which causes a shortage of goods (quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied), or a minimum market price (floor), which causes a surplus (quantity supplied is greater. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? There are two types of price controls: Maximum price that the good has ever sold for. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. * introduction * price floors and price ceilings are price controls, examples of * why government uses price controls? Just like price ceilings , price floors are intended to help some people but generate predictable and undesirable side effects. Say our price is $4.32 and we need to round it down to the nearest value divisible by 5 cents, the floor function would read where the number is your starting point and the significance is the multiple you want your number rounded down to for floor, or up to for ceiling. Price ceilings and price floors. If demand shifts from d0 to d1, the new equilibrium would be at e1—unless. Philippines price floor to ceiling windows aluminum alloy sliding glass window powder coated aluminum sliding windows. By this definition, the term ceiling has a pretty intuitive interpretation, and this is illustrated in the diagram above. Price floors and price ceilings are price controls, examples of government intervention in the free market which changes the market equilibrium. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling.
4 5 Price Controls Principles Of Microeconomics
Price Floor Wikipedia. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors.
Sample 5 6 Pdf 1 A Price That The Government Guarantees Farmers Will Receive For A Particular Crop Is A A Price Ceiling B A Price Floor Price Support Course Hero
Price Ceiling And Price Floor. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity.
Price Controls In A Competitive Industry And Monopoly Markets
Price Floor And Price Ceiling Concepts Pros And Cons. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling. $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity.
Kebijakan Price Floor Dan Price Ceiling Twenty Two Pm
Effects Of Price Control By Government. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0.
Price Ceiling Price Floor Sidik S Blog
Price Controls In A Competitive Industry And Monopoly Markets. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism.
Price Ceilings And Floors Micro Topic 2 8 Youtube
Price Controls In A Competitive Industry And Monopoly Markets. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0.
Solutions To Price Ceiling And Price Floor In Malaysia Buffer Stock Scheme Black Market Economies
Reading Inefficiency Of Price Floors And Price Ceilings Microeconomics. What happens when the government, not a market, sets the price? Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of quantity. A price floorthe minimum price at the theory of price floors and ceilings is readily articulated with simple supply and demand analysis. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. The difference between a price ceiling and a price floor. Pf d qd q< qs q $169 $69 p qd of qs of seats < seatss $169 a price floor causes a. 5.4 price floors and ceilings. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied, qs, exceeds the remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. $169 $69 s p whenever there is $169 a price floor $69 p the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. A price ceiling example—rent control the original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e0. Consider a price floor—a minimum legal price. A price floor is the lowest possible selling price, beyond which the seller is not willing or not able (legally) to sell the product. Price ceiling—the highest price the seller can sell the product. However, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e0 and prevents it from falling.