Price Ceiling Calculate Shortage
Pictures. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. It's generally applied to consumer staples. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? Calculate effects of price floor. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service.
Animation On How To Calculate Price Floors With Calculations Youtube
4 5 Price Controls Principles Of Microeconomics. It's generally applied to consumer staples. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Calculate effects of price floor. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result.
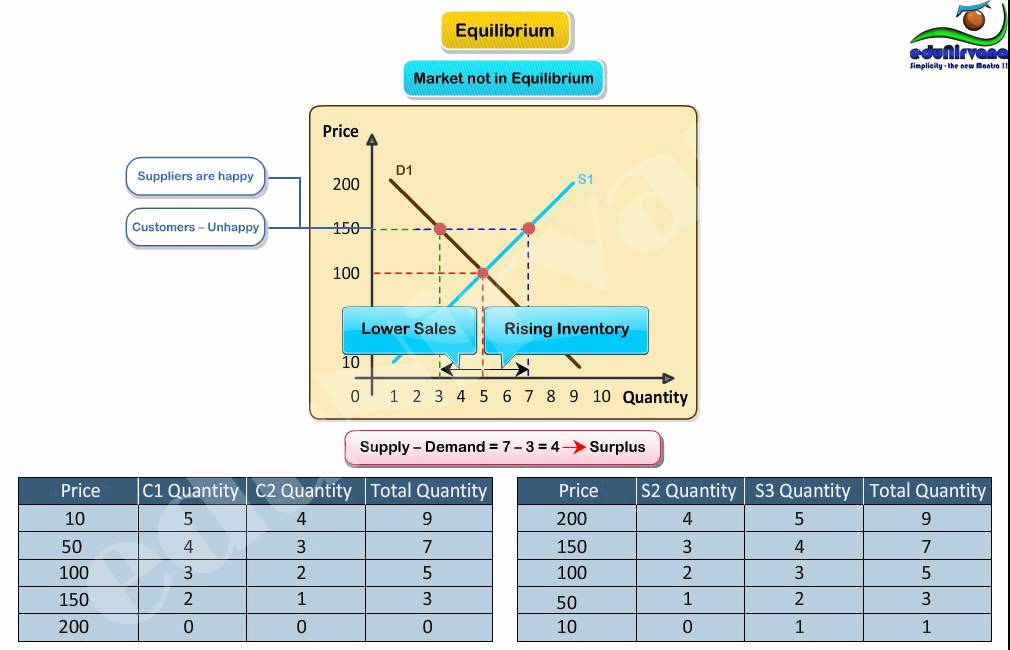
Supply & demand with a price ceiling; Governments intend price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make necessary commodities unattainable. When the price of cd increased from $20 to $22, the quantity of cds demanded decreased from 100 to 87. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Price ceiling = 4.5 shortage: When a price ceiling is set, a shortage occurs. Calculating price elasticity of demand:
Why exactly does a price ceiling cause a shortage?
The shortages created by price ceilings can be resolved in many ways without increasing the price. In order for a price ceiling to be effective, it must be set below the natural market equilibrium. Analyze demand and supply as a social adjustment mechanism. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. The shortages created by price ceilings can be resolved in many ways without increasing the price. A price ceiling is a legal maximum price that one pays for some good or service. Why exactly does a price ceiling cause a shortage? Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Price ceilings and price floors. This is the most common way of resolving the shortage, wherein, the person who comes first gets to buy the product. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. But depending on the market demand for apartments, this price ceiling could hinder supply and create inefficiencies and shortages in the market. In this topic learn about the unintended consequences of price ceilings, shortages and quality reduction. A price ceiling means that the price of a good or service cannot go higher than the regulated this results in a shortage because quantity demanded is higher than quantity supplied. Buyers now are faced with a potential shortage of the product and may even be forced to secure the product through illegal means, such as looking in to the black market. And sellers can discriminate at lower cost, or even at no cost. Price elasticity of demand is a measurement that determines how demand for goods or services may change in response to a change in the prices of those goods or services. Does a price ceiling change the equilibrium price? Finally, the price elasticity of demand is calculated by dividing the expression in step 2 by expression in step 3 as shown below. When the price of cd increased from $20 to $22, the quantity of cds demanded decreased from 100 to 87. Assume a linear demand function of the form: How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. / % change in price. A price ceiling occurs when the government puts a legal limit on how high the price of a product can be. Supply & demand with a price ceiling; It is called a price ceiling because the for an example where price controls do not cause shortages, see this post about consumer and producer surplus with perfectly inelastic supply. Calculating price elasticity of demand: A price ceiling is when the government sets a maximum price that firms are allowed to charge for a good or service. How to calculate price elasticity of demand. Price ceiling = 4.5 shortage: A government imposes price ceilings in order to keep the price when a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, as in this example, it is considered a binding price ceiling, thereby resulting in a shortage.
4 5 Price Controls Principles Of Microeconomics
Graph Market Surplus And Shortage Youtube. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. It's generally applied to consumer staples. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Calculate effects of price floor. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service.
Price Floors And Ceilings
Solved Calculate The Shortage Surplus Created By The Pr Chegg Com. Calculate effects of price floor. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. It's generally applied to consumer staples.
Chapter Five Government Intervention Kieran Bellew S Blog
What Is A Price Ceiling. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Calculate effects of price floor. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service.
What Is A Price Ceiling
Price Ceiling Shortage Calculation Pregnancy Test Kit. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Assume a linear demand function of the form: A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Calculate effects of price floor. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. It's generally applied to consumer staples. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations.
Chapter 7 Flashcards Quizlet
Price Ceilings Shortages Quality Reductions Microeconomics Videos. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Assume a linear demand function of the form: Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Calculate effects of price floor. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. It's generally applied to consumer staples. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient.
Solved 1 Point 5 Calculate The Amount Of The Shortage Or Chegg Com
What Is A Price Ceiling. One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive. Assume a linear demand function of the form: It's generally applied to consumer staples. Calculate effects of price floor. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics.
Price Ceiling Shortage Calculation Pregnancy Test Kit
Econowaugh Ap 2015 Ap Microeconomics Exam Frq 3. Animation on how to calculate price floors with calculations. A price ceiling is a maximum amount, mandated by law, that a seller can charge for a product or service. Using the supply and demand curve, we show how price ceilings lead to a shortage of goods and to low. Just because a price ceiling is enacted in a market, however, doesn't mean that the market outcome will change as a result. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. Calculate effects of price floor. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity in the price ceiling example, if someone were to ask how large the shortage is in this scenario, would the answer be 4,000 rental units? One of the arguments against setting price ceilings is that the shortage created by price ceilings actually makes it difficult to find and purchase sufficient. Assume a linear demand function of the form: It's generally applied to consumer staples. How to calculate an equilibrium equation in economics. When demand exceeds supply at the price that is sustained in a market, a shortage results. Price ceilings result in five major unintended consequences, and in this video we cover two of them. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. Governments use price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make commodities prohibitively expensive.