Get Price Ceiling Demand And Supply Curve
Pics. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? Price ceilings and price floors. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result.
Market Equilibrium
The Upward Trend In Medical Mask Prices Is There Room For Ethics In Economics Citizen C Post Detail Concordia International School Shanghai Jinqiao China. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. Price ceilings and price floors. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good.
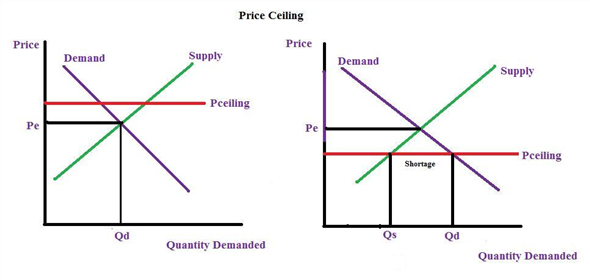
A price ceiling can be illustrated by the normal demand and supply curves. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. What factors affect the elasticity of supply? It is truly a balance of the. We can easily show that price ceilings create shortages using our standard demand and supply framework. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. This results in excess of quantity demanded over quantity supplied thus creating shortage in the market.
While the supply curve for agricultural goods has shifted to the right, the demand has increased with rising population and with rising income.
A price ceiling of p3 causes Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result. Price ceilings and price floors. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. 8.2 generally, price ceilings reduce seller incentives to prepare for demand and supply shocks, but the story is a little more complicated. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. Production costs factors increasing supply and shifting the supply curve to the right: The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. While the supply curve for agricultural goods has shifted to the right, the demand has increased with rising population and with rising income. A price ceiling occurs when the government puts a legal limit on how high the price of a product can be. Producer's surplus is the area above the supply curve and below the market price line. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? Reading over to the demand curve, we find that consumers would like to rent a2 apartments at the price ceiling of pc. Explain price controls, price ceilings, and price floors. The following two questions refer to the supply and demand curves illustrated below. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. The demand and supply curve intersect and form the market equilibrium. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. By determining where the new equilibrium is relative to the initial. This results in increased demand of the commodity than the quantity supplied. What factors affect the elasticity of supply? Consequently, marginal costs are exceeded by marginal benefits resulting in. P* shows the legal price the government has set. Markets in action price ceilings a price ceiling is a government regulation of the maximum price that may be legally charged. In this video i use ms excel 2010 to plot demand curve and supply curve to find equilibrium price and quantity graphically. Price ceiling (also known as price cap) is an upper limit imposed by government or another statutory body on the price of a product or a service. An exchange of a product takes place when price determination depends equally on demand and supply. Market equilibrium is the point at which the quantity supplied to the marketplace equals the quantity demanded by consumers in the marketplace. Demand and supply represent the willingness of consumers and producers to engage in buying and selling.
Price Controls Maximum And Minimum Price
The Law Of Supply And The Supply Curve. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. Price ceilings and price floors.
Animation On How To Price Floors And Price Ceilings Youtube
Principles Of Microeconomics Price Ceilings And Price Floors Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. Price ceilings and price floors. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control.
What Is Price Floor Definition Of Price Floor Price Floor Meaning The Economic Times
90 Economy Ideas Economy Economics Macroeconomics. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. Price ceilings and price floors. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good. Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result.
Price Floor Wikipedia
Solved If With The Demand And Supply Curves Shown The G Chegg Com. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Price ceilings and price floors. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily.
The Penicillin Price Ceiling Scientific Diagram
3 5 Demand Supply And Efficiency Texas Gateway. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good. Price ceilings and price floors. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change.
Price Ceiling In Supply Demand Curve Scientific Diagram
4 5 Price Controls Principles Of Microeconomics. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. Price ceilings and price floors. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market.
Price Floor And Tax On Cheese Market
Econ 150 Microeconomics. Supply and demand curve are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. Price ceilings have been proposed for other products, for example, for prescription drugs, doctor and. Price ceilings can be advantageous in allowing essentials to be affordable, at least temporarily. Price controls can cause a different choice of quantity supplied along a supply curve, but they do not shift the supply curve. Economists believe there are a small number of fundamental principles that however, the underlying forces that shifted the demand curve to the right are still there. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good. As supplies fell short of demand, shortages developed and rationing was often imposed through schemes like alternating days in which only cars. They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market. How does quantity demanded react to artificial constraints on price? In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, and excess demand or shortages will result. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity. A price ceiling is essentially a type of price control. Price ceilings and price floors. Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change.